By: Markita Lewis, MS, RD
Having healthy skin doesn’t just mean that you have youthful-looking skin. Many of the important functions of skin happen right beneath the surface.
In recent years, skincare has become one of the fastest-growing industries in beauty as more people want to protect their skin from premature aging and damage. Collagen is one of the most popular dietary supplements for youthful skin, but is it truly effective for achieving healthy skin?
In this article you’ll discover:
- What is collagen?
- Collagen’s role in the skin
- The benefits of collagen for skin health
- How much collagen is effective for healthy skin?
- Other ways to support healthy skin
If you’ve ever wondered if collagen supplements were worth the hype for skincare, continue reading.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body and quite literally, helps keep you put together. Collagen makes up the connective tissues in your body and is found in your skin, bones, hair, nails, tendons, cartilage, and muscles. However, collagen is an incomplete protein and lacks the essential amino acid, tryptophan.
Our bodies are able to naturally produce collagen by combining amino acids (glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline), vitamin C, and copper. The resulting structure is a tightly coiled triple helix-shaped protein.1
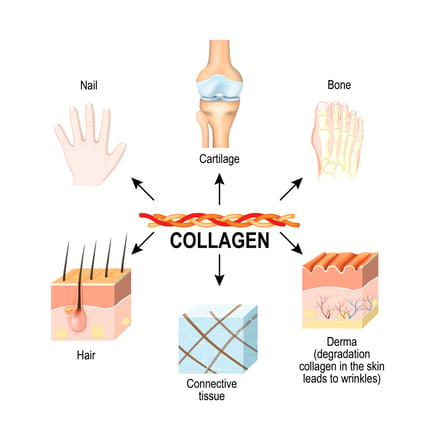
Collagen’s Role in the Skin
Now that you know what collagen is, let’s take a look at its role in maintaining the structure of our skin.
The skin’s major role is to protect the body from pollutants, injuries, and microorganisms that can cause harm to your body. It is made of three major layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis. Each of these layers has its own functions.2
The functions of these skin layers include:
- Epidermis: Protects against external elements, contains melanin, supports immune function, and makes new skin.
- Dermis: Maintains the skin’s shape, grows hair, houses nerve receptors for touch, supplies blood to the epidermis, produces sweat, and makes oil.
- Hypodermis: Connects the skin to muscles and bones, regulates body temperature, cushions muscles and bones from injury, and supports nerve and blood vessels.
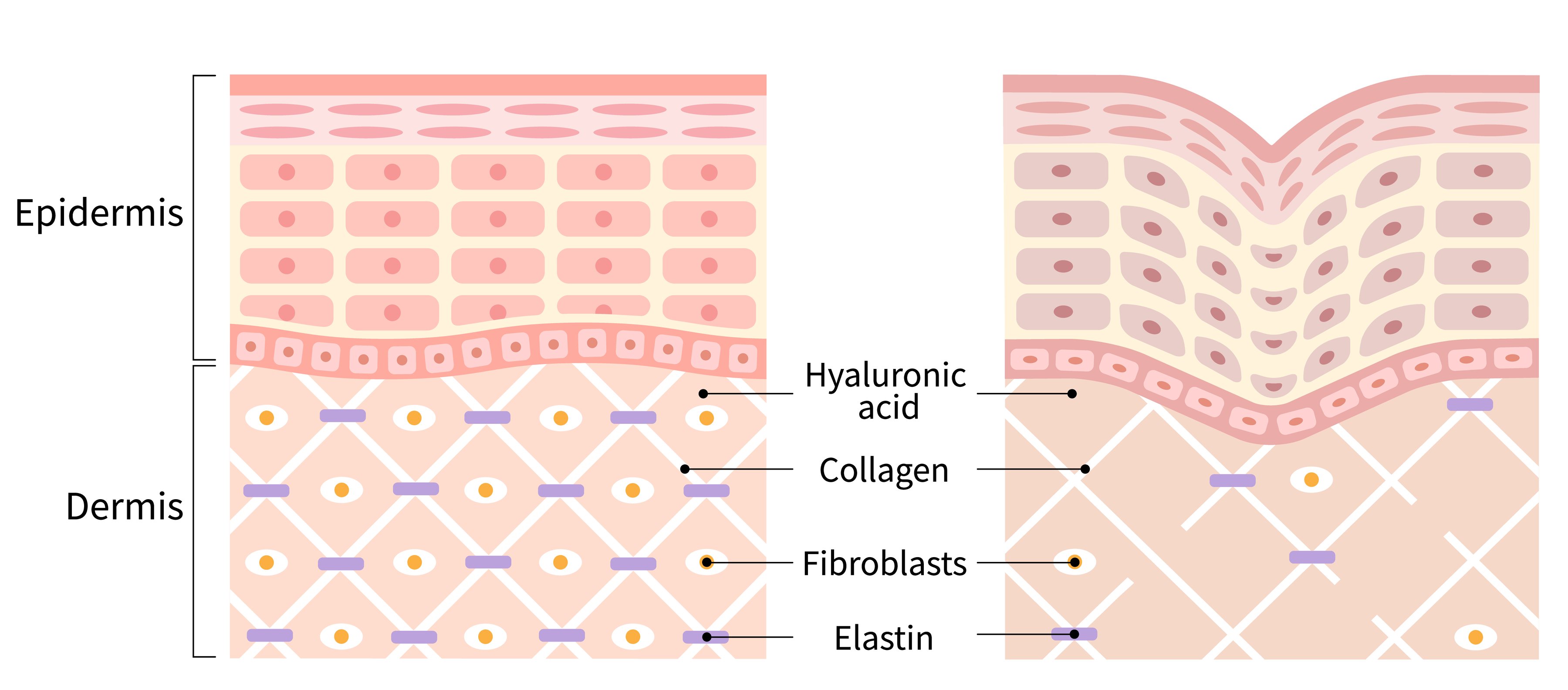
The dermis is mostly made of an extracellular matrix that consists of collagen and elastic fibers. This matrix maintains skin structure, moisture retention, and the general function of the skin. Collagen supports the strength and resilience of the dermis skin layer against UV damage, pollution, and nutrient deficiencies.
If collagen levels decrease within the dermis, this can cause the skin to lose moisture and elasticity. As a result, skin can have wrinkles, be rough to the touch, and be prone to sagging.3
Benefits of Collagen for Skin
While we can naturally produce collagen in our bodies, we become less efficient at making collagen after around age 25. This can impact not only our skin’s health but the other connective tissues in our body. This is where collagen supplements can lend a hand in maintaining healthy skin.3
Skin Hydration
Some research found that taking an oral collagen supplement improved the collagen density within the skin and significantly improved skin hydration after eight weeks.4 Collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen can also support skin hydration through the synthesis of hyaluronic acid, a natural substance found in the skin that binds to water molecules and maintains skin hydration.5
Skin Elasticity
Skin elasticity is the skin’s ability to stretch and snap back to its regular state. In well-hydrated and younger skin, there is high elasticity. However, older skin that has lost its elasticity may look or feel saggy, leathery, or have a wrinkled appearance. Multiple studies find that taking a collagen peptide supplement is effective for improving skin elasticity in people with visibly aged skin.6
Reducing Wrinkles
Wrinkles are a visible sign of skin aging and occur as skin progressively loses its hydration, elasticity, and collagen stores. In a 12-week study with women aged 45-54 years, supplementation with freshwater marine collagen significantly improved skin wrinkles and firmness when compared to a placebo.7 In a 12 week, double blind trial in 128 women aged 39-59 years, oral supplementation containing 500 mg of Biocell Collagen composed of hydrolyzed collagen type II, hyaluronic acid, and chondroitin sulfate resulted in significant improvements in facial lines and wrinkles, crow’s feet lines, skin collagen content, and skin elasticity compared to the group taking a placebo.
Overall, collagen supplements appear to be effective for supporting skin health. A recent 2020 review found that taking hydrolyzed collagen, also called collagen peptides for skin health was consistent in improving signs of skin aging.8 This improvement is dependent on regularly taking collagen for at least several weeks, so if you discontinue collagen peptides then you may see a return to your pre-supplement skin status.
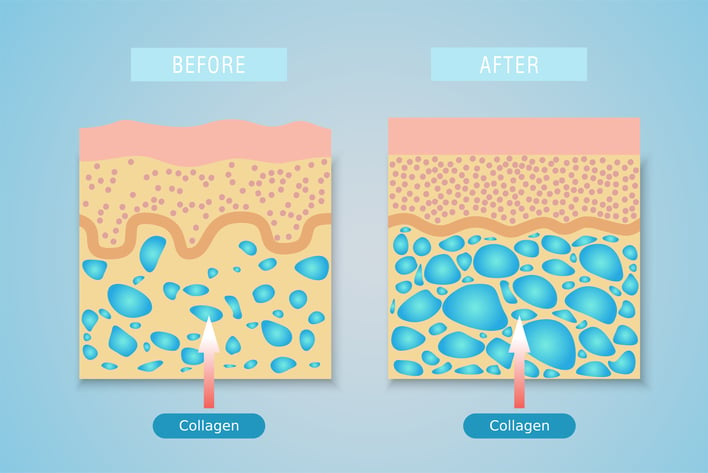
How Much Collagen Should You Take for Skin Health?
There isn’t a standard amount of collagen that you need to take in order to see improvements in your skin health. Studies have found daily collagen intake between 2.5 and 10 grams to be effective for people of different ages. Other studies have shown smaller amounts of hydrolyzed collagen peptides combined with other skin supporting ingredients to be beneficial. How much collagen you need to see benefits for your skin may depend on the current health of your skin and your age.
Collagen supplements also aren’t an instant miracle worker for your skin. It can take at least 6 to 8 weeks of regular supplementation in order to experience a notable difference in your skin.
To make the most out of your collagen supplement, be sure to choose one that contains collagen peptides, hydrolyzed collagen, or collagen hydrolysate. Collagen peptides are smaller in size so that they are more bioavailable and easily absorbed into the body. Other ingredients including hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate play a role in supporting skin health.
Collagen supplementation is considered safe. However, the addition of herbs may cause adverse reactions or interfere with medication. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult with their doctor prior to taking collagen supplements.
Other Ways to Support Healthy Skin
Collagen peptides are an effective supplement for skin health and can be combined with other lifestyle habits to support youthful and healthy skin.
Top ways to support healthy skin include:
- Stop smoking: Smoking increases oxidative stress on the skin, decreases skin elasticity and skin density, and increases your risk for skin cancer.10
- Wear sunscreen: Photoaging, or skin damage caused by exposure to UVA and UVB rays, can significantly age skin. Regularly using sunscreen can protect the skin from UV rays and slow down premature skin aging.11
- Have a regular sleep schedule: Beauty sleep may have more truth to it than you’d think. When you sleep, stress hormones decrease and blood flow to the skin increases, which allows for skin repair.
- Eat a healthy diet: In order to have healthy skin, your skin cells need a variety of nutrients including protein, vitamins, and minerals. Eating a diet filled with nutrient-dense whole foods can support healthy skin.12
- Stay hydrated: Inadequate water intake can decrease the amount of water in your skin and make your skin dry and dehydrated. Drinking at least 2 L of water daily can help with normal skin hydration.12
- Have an exercise routine: Exercising improves blood flow to the skin, which allows for faster delivery of nutrients and removal of wastes, and generally slows down cell aging.13
Summary
Collagen lives up to the hype as a supplement for skin health. Combined with healthy lifestyle habits, you can help your skin stay healthy and reduce the risk of premature skin aging. When compared to topical products, oral supplementation with collagen peptides have shown greater effects on skin or what is often referred to as “beauty from within,“ especially when combined with certain vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.14
References
- Shoulders MD, Raines RT. Collagen structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:929-958. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.032207.120833
- Kolarsick, PAJ ; Kolarsick, MA; Goodwin, C. Anatomy and physiology of the skin, J. Dermatol. Nurses’ Assoc. 2011; 3(4): 203-213. doi: 10.1097/JDN.0b013e3182274a98
- Russell-Goldman E, Murphy GF. The Pathobiology of Skin Aging: New Insights into an Old Dilemma. Am J Pathol. 2020;190(7):1356-1369. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.03.007
- Asserin J, Lati E, Shioya T, Prawitt J. The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14(4):291-301. doi:10.1111/jocd.12174
- Kang MC, Yumnam S, Kim SY. Oral Intake of Collagen Peptide Attenuates Ultraviolet B Irradiation-Induced Skin Dehydration In Vivo by Regulating Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3551. Published 2018 Nov 11. doi:10.3390/ijms19113551
- Jhawar N, Wang JV, Saedi N. Oral collagen supplementation for skin aging: A fad or the future?. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19(4):910-912. doi:10.1111/jocd.13096
- Evans M, Lewis ED, Zakaria N, Pelipyagina T, Guthrie N. A randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel study to evaluate the efficacy of a freshwater marine collagen on skin wrinkles and elasticity. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(3):825-834. doi:10.1111/jocd.13676
- Schwartz SR, Hammon KA, Gafner A, Dahl A, Guttman N, Fong M, Schauss AG. Novel Hydrolyzed Chicken Sternal Cartilage Extract Improves Facial Epidermis and Connective Tissue in Healthy Adult Females: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Altern Ther Health Med. 2019 Sep;25(5):12-29. PMID: 31221944.
- Barati M, Jabbari M, Navekar R, et al. Collagen supplementation for skin health: A mechanistic systematic review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19(11):2820-2829. doi:10.1111/jocd.13435
- Yazdanparast T, Hassanzadeh H, Nasrollahi SA, et al. Cigarettes Smoking and Skin: A Comparison Study of the Biophysical Properties of Skin in Smokers and Non-Smokers. Tanaffos. 2019;18(2):163-168.
- Shanbhag S, Nayak A, Narayan R, Nayak UY. Anti-aging and Sunscreens: Paradigm Shift in Cosmetics. Adv Pharm Bull. 2019;9(3):348-359. doi:10.15171/apb.2019.042
- Cao C, Xiao Z, Wu Y, Ge C. Diet and Skin Aging-From the Perspective of Food Nutrition. Nutrients. 2020;12(3):870. Published 2020 Mar 24. doi:10.3390/nu12030870
- Rebelo-Marques A, De Sousa Lages A, Andrade R, et al. Aging Hallmarks: The Benefits of Physical Exercise. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:258. Published 2018 May 25. doi:10.3389/fendo.2018.00258
- Maia Campos, P.M.B.G.; Melo, M.O.; Siqueira César, F.C. Topical application and oral supplementation of peptides in the
improvement of skin viscoelasticity and density. J. Cosmet. Derm. 2019, 18, 1693–1699


